Printable Sudoku
- Alphabet
- Battleships
- Binary
- Bridges / Hashi
- Chain Sudoku
- Consecutive
- Cross Sudoku
- Flower Sudoku
- Frame Sudoku
- Futoshiki
- Galaxies
- Greater Than
- Hitori
- Jigsaw Sudoku
- Kakuro
- KenKen
- Killer Sudoku
- Kropki Sudoku
- Little Killer
- Magic Squares
- Nonogram
- Odd Even Sudoku
- Outside Sudoku
- Rossini Sudoku
- Samurai Sudoku
- Sandwich
- Skyscraper
- Slitherlink
- Sohei Sudoku
- Star Battle
- Sudoku
- Sudoku for Kids
- Sudoku Mine
- Sudoku XV
- Sujiken
- Tripledoku
- Tripod Sudoku
- Twodoku
- Vudoku
- Windmill
Special Variations
Generate
Play / Solve
- Home»
- Consecutive
Consecutive Sudoku Puzzles
Download free printable Consecutive Sudoku puzzles in PDF format! These puzzles come in different difficulty levels, so you can choose the one that suits you best. Download them and enjoy solving Sudoku offline anytime you like.
Showing 1-15 of 70 records
Sort by:
Consecutive Sudoku - Medium - 4
Consecutive Sudoku - Medium - 1
Consecutive Sudoku - Medium - 3
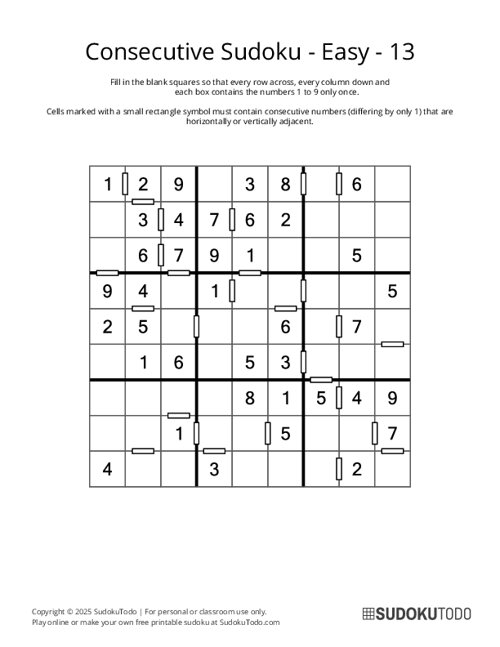
Consecutive Sudoku - Easy - 13
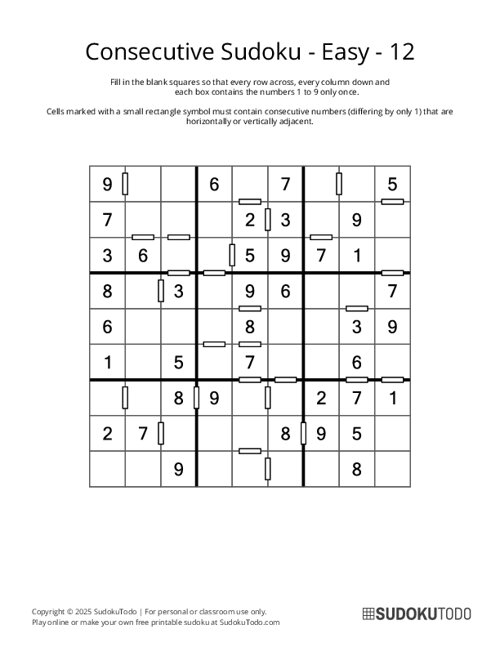
Consecutive Sudoku - Easy - 12
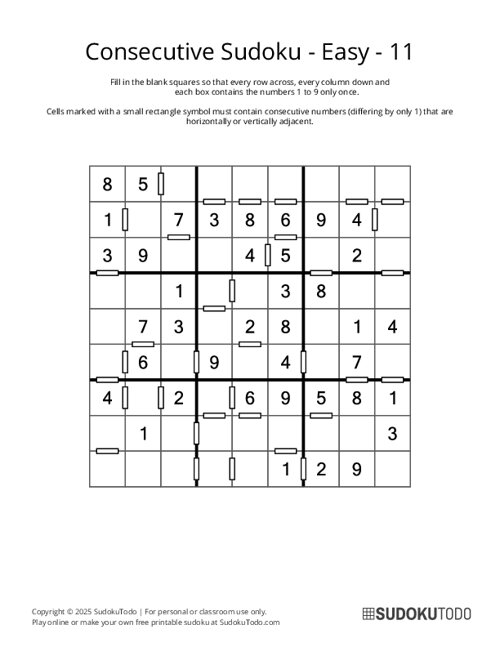
Consecutive Sudoku - Easy - 11
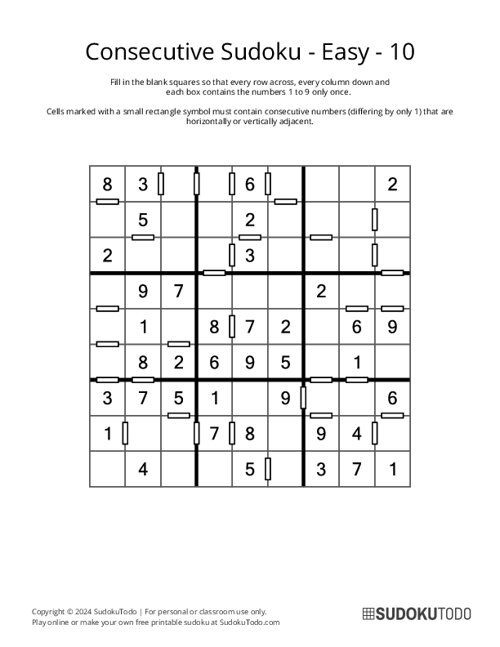
Consecutive Sudoku - Easy - 10
Consecutive Sudoku - Easy - 9
Consecutive Sudoku - Hard - 7
Consecutive Sudoku - Medium - 2
Consecutive Sudoku - Medium - 5
Consecutive Sudoku - Medium - 6
Consecutive Sudoku - Medium - 7
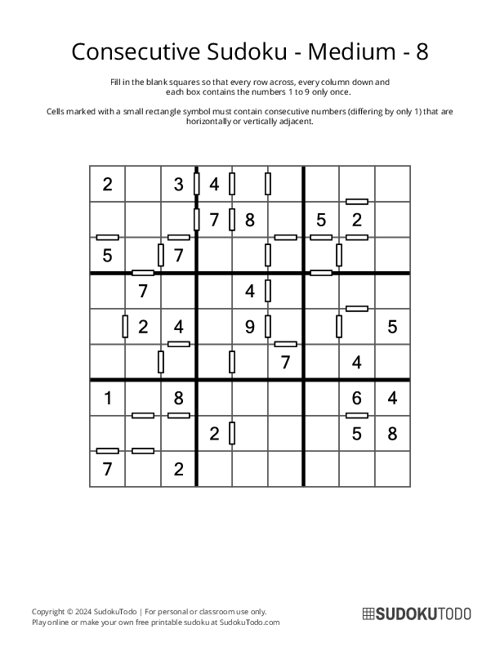
Consecutive Sudoku - Medium - 8
Consecutive Sudoku - Medium - 9
About Consecutive Sudoku Puzzles
A Consecutive Sudoku is a special version of the regular Sudoku puzzle. It follows all the usual Sudoku rules, but it adds an extra challenge. In this variation, some pairs of neighboring cells have special markers between them, like bars or circles. These markers show that the numbers in those two cells must be consecutive, meaning they are next to each other in order, like 3 and 4 or 7 and 8. This extra rule makes the puzzle a bit more challenging and fun!
Consecutive Sudoku is also known by names like Successor Sudoku, Sequential Sudoku, or 1-away Disallowed Number Place.
Rules / How to Play
- Grid Size: The puzzle has 9x9 grid size made up of three 3x3 sub-grids.
- Numbers: Each row, column, and 3x3 box must contain the digits 1 through 9.
- No Repetition: Each row, column, and 3x3 subgrid (in a 9x9 puzzle) must contain all digits from 1 to 9 without repetition.
- Consecutive Markings: If two adjacent cells (horizontally or vertically) are marked with a bar or circle, their values must differ by exactly 1. Also, if there is no mark between two adjacent cells, their values cannot differ by 1.
- Diagonal Rules: Diagonal cells are not required to have consecutive numbers unless it is specifically mentioned. Cells without any marks (up or down, left or right) cannot have consecutive numbers.
Solving Tips and Techniques:
In addition to the standard Sudoku techniques, here are some strategies specific to Consecutive Sudoku.
- Look for Constraints: If a cell in a consecutive pair already has a number, the other cell's number is automatically determined. For example, if one cell in a pair contains a 7, the other must be a 6 or an 8.
- Start with Limited Candidates: A cell marked with a 1 must have its adjacent marked cell as 2, and vice versa. Similarly, 8 pairs only with 7 or 9, 9 pairs only with 8, etc.
- Elimination: If a number is already in a row, column, or box, it can't appear right next to another number in the same group. For example, if a 5 is already in a row and one cell in a pair in that row has a 4, the other cell in the pair can't be a 5.
- Chain Reasoning: By looking at several connected pairs, you can figure out the possible values for cells farther down the line. For example, if one cell in a pair is 2, and a cell in the next pair is 4, you can work out that the other cells in the chain must be 1, 3, and 5.
- Hidden Pairs: Check for cells in a row, column, or box that can only have two or three specific numbers. This helps rule out other numbers for those cells.
By using these techniques together, you can solve even the toughest Consecutive Sudoku puzzles step by step, in an organized and systematic way!