Printable Sudoku
- Alphabet
- Battleships
- Binary
- Bridges / Hashi
- Chain Sudoku
- Consecutive
- Cross Sudoku
- Flower Sudoku
- Frame Sudoku
- Futoshiki
- Galaxies
- Greater Than
- Hitori
- Jigsaw Sudoku
- Kakuro
- KenKen
- Killer Sudoku
- Kropki Sudoku
- Little Killer
- Magic Squares
- Nonogram
- Odd Even Sudoku
- Outside Sudoku
- Rossini Sudoku
- Samurai Sudoku
- Sandwich
- Skyscraper
- Slitherlink
- Sohei Sudoku
- Star Battle
- Sudoku
- Sudoku for Kids
- Sudoku Mine
- Sudoku XV
- Sujiken
- Tripledoku
- Tripod Sudoku
- Twodoku
- Vudoku
- Windmill
Special Variations
Generate
Play / Solve
- Home»
- Chain Sudoku»
- Easy
Easy Chain Sudoku Puzzles
Download and print easy Chain Sudoku puzzles for hours of fun! Perfect for beginners, these printable puzzles feature simple solutions and are ideal for sharpening your mind. Simply download, print, and start solving with a pen or pencil!
Showing 1-15 of 60 records
Sort by:
9x9 Chain Sudoku - Easy - 2
5x5 Chain Sudoku - Easy - 4
5x5 Chain Sudoku - Easy - 5
5x5 Chain Sudoku - Easy - 8
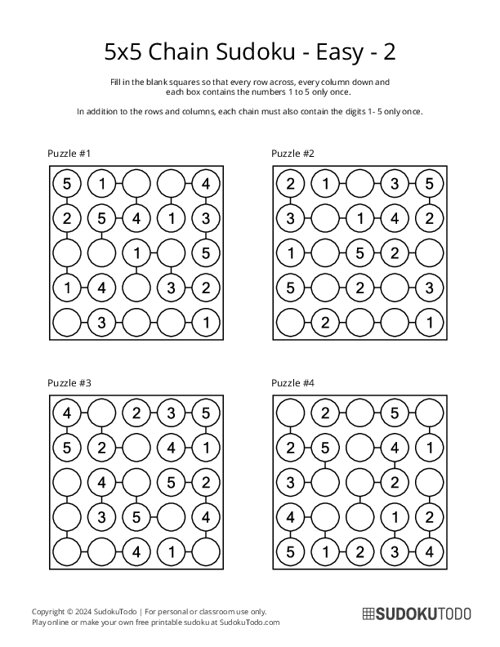
5x5 Chain Sudoku - Easy - 2
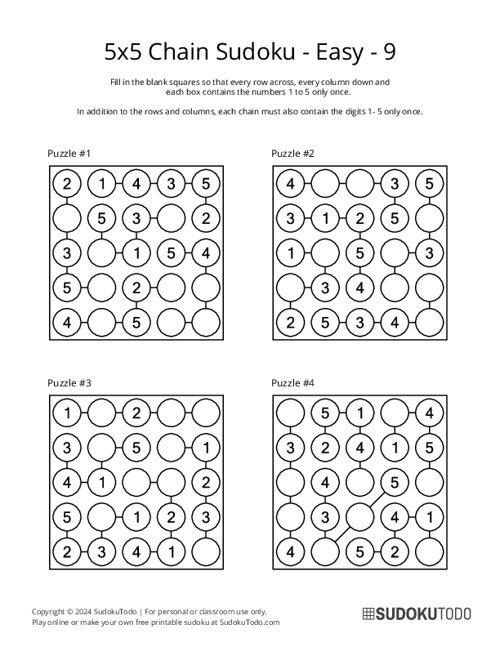
5x5 Chain Sudoku - Easy - 9
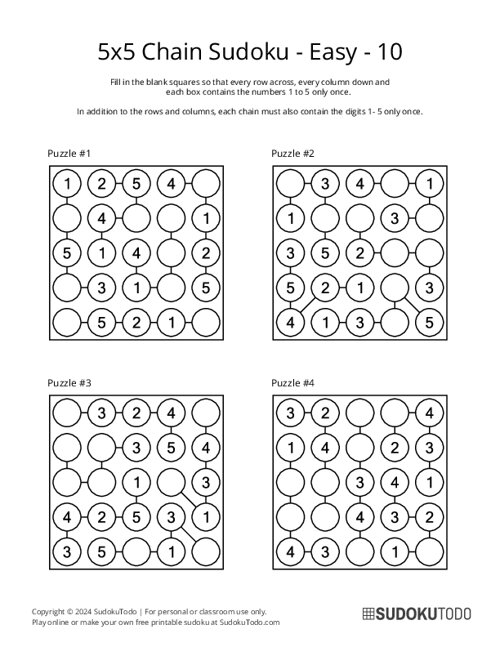
5x5 Chain Sudoku - Easy - 10
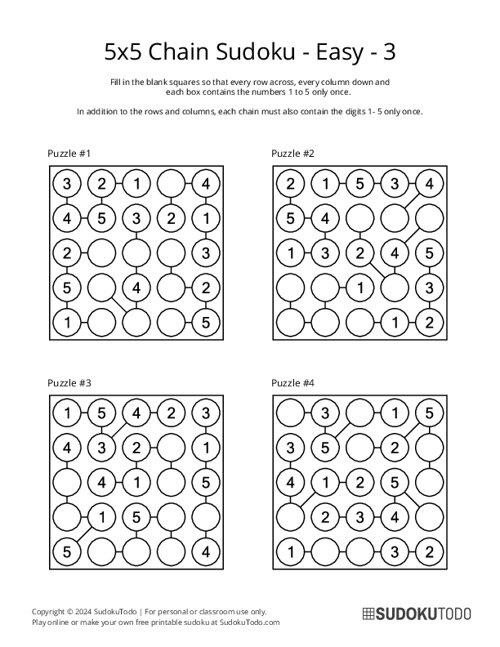
5x5 Chain Sudoku - Easy - 3
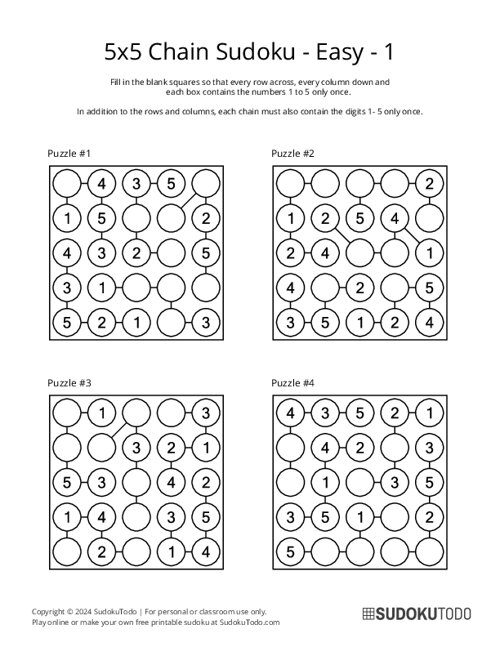
5x5 Chain Sudoku - Easy - 1
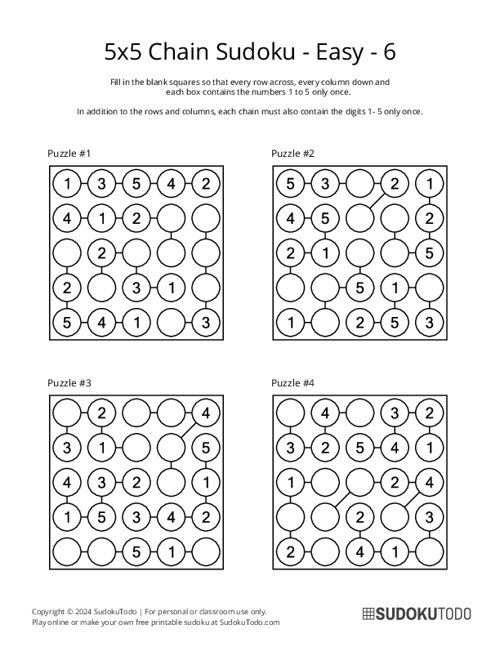
5x5 Chain Sudoku - Easy - 6
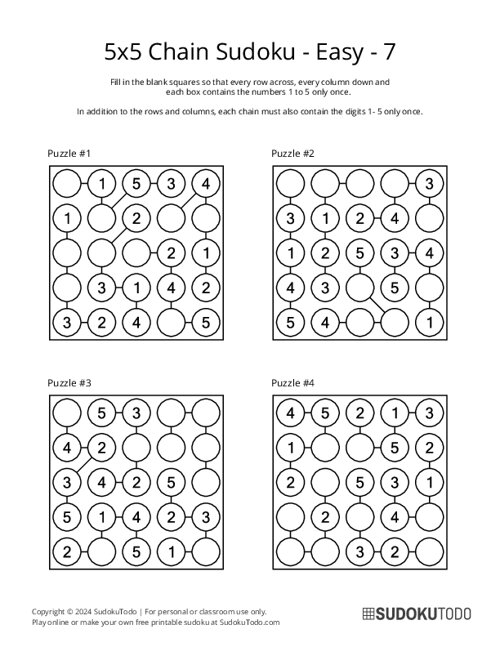
5x5 Chain Sudoku - Easy - 7
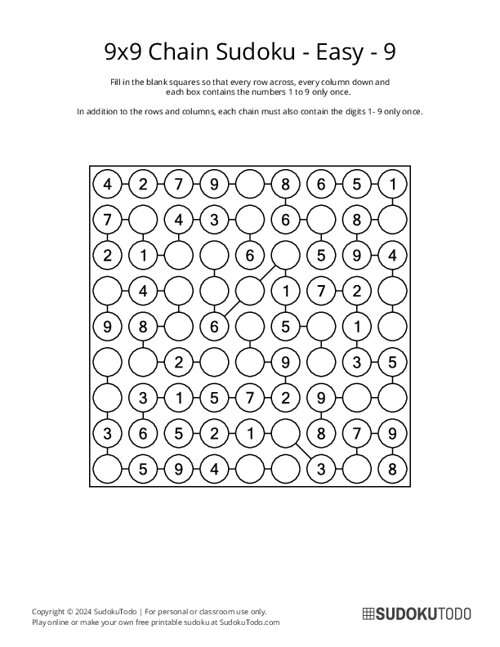
9x9 Chain Sudoku - Easy - 9
9x9 Chain Sudoku - Easy - 3
9x9 Chain Sudoku - Easy - 4
9x9 Chain Sudoku - Easy - 1
About Chain Sudoku Puzzles
"Chain Sudoku," also known as "Strimko," is a logic puzzle where you fill circles arranged in a square grid with digits. In this version, there is a new rule involving something called "chains." A chain is a group of connected cells in the puzzle, and these cells must contain numbers that follow each other in order, like 1, 2, 3 or 5, 6, 7.
Basic Rules
- Layout: The grid is a N x N board containing circle cells connected by lines (chains).
- Unique Numbers: Each digit from 1-9 must appear exactly once in each row and column of the grid.
Chain Rules
Certain cells are linked by chains, indicated by lines connecting the cells. Each chain may have a specific rule, such as:
- Equality: All the cells in the chain must have the same number.
- Sequential Numbers: The numbers in the chain must be in order, like 2, 3, 4 or 5, 6, 7.
- Arithmetic Rule: The numbers in the chain must follow a math rule, like each number being the sum of its neighbors or having a fixed difference between them.
Solving Tips and Techniques:
Besides the usual methods used to solve regular Sudoku, Chain Sudoku needs some extra strategies.
- Identify Chains: Find cells where only two numbers can go. If you see two cells with the exact same two numbers as options, they might belong to a chain.
- Elimination: When you find a chain in the puzzle, you can narrow down the possible numbers for the other cells in that chain. For example, if one cell in the chain can only be a 3 or a 4, then no other cell in the chain can be a 3 or a 4.
- Use Chain Logic: You can use chain logic to solve harder puzzles. For example, if three connected cells in a chain must have the numbers 1, 2, and 3, you can use this clue to figure out where these numbers can't go in other parts of the puzzle. This helps narrow down the possibilities and makes solving the puzzle easier.
Chain Sudoku puzzles are fun and challenging, giving you more to think about than regular Sudoku. You still use the basic Sudoku rules, but the chains make you plan even more carefully. This extra challenge makes them a popular choice for people who love solving tricky puzzles!